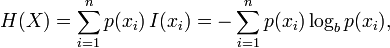The entropy H of a discrete random variable X with possible values {x1, ..., xn} is
Here E is the expected value function, and I(X) is the information content or self-information of X.
I(X) is itself a random variable. If p denotes the probability mass function of X then the entropy can explicitly be written as
where b is the base of the logarithm used. Common values of b are 2, Euler's number e, and 10, and the unit of entropy is bit for b = 2, nat for b = e, and dit (or digit) for b = 10.[3]
In the case of pi = 0 for some i, the value of the corresponding summand 0 logb 0 is taken to be 0, which is consistent with the limit